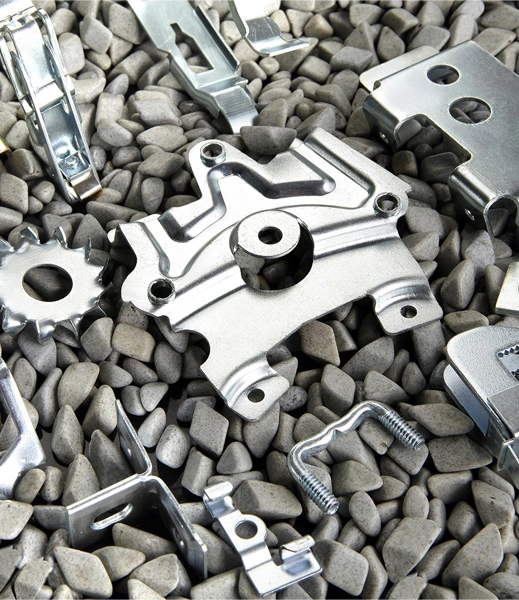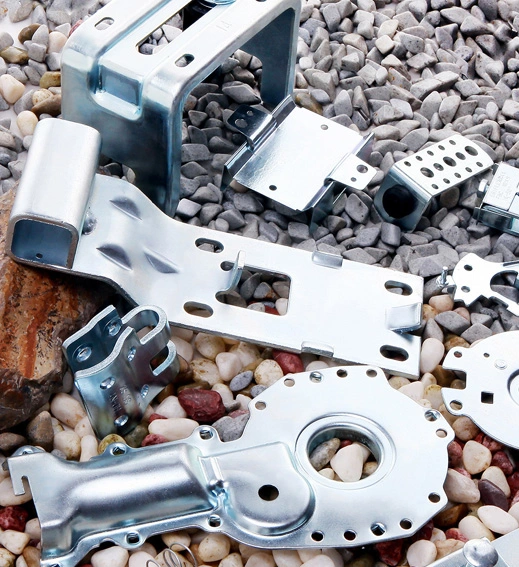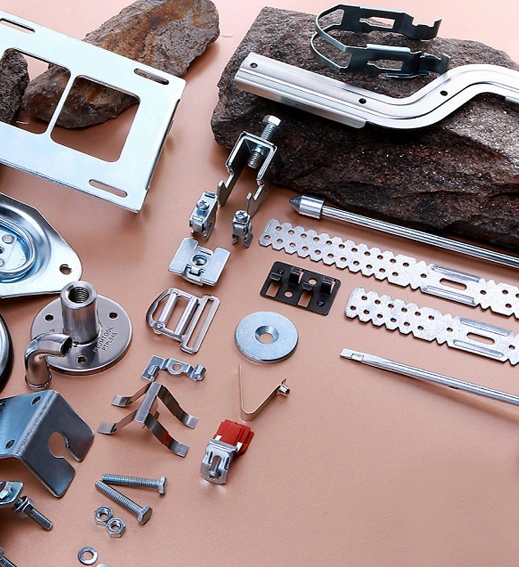

Matériau: Acier Zinc plaqué
Surface: Zinc plaqué/peinture
Taille personnalisée
Tolérance: ± 0.025mm
Chine emboutissage de pièces automobiles, formant la forme du couvercle métallique par le moule, poinçonnage et découpage d'automobile, poinçonnage d'estampage
Stamping materials are important factors that affect the quality of parts and the lifespan of molds. At present, Stamping materials not only include low-carbon steel, but also stainless steel, aluminum and aluminum alloys, copper and copper alloys, etc.
Steel plate is currently the most widely used raw material in automotive stamping. With the requirement for lightweight bodies, new materials such as high-strength steel plates and sandwich steel plates are increasingly used in automotive bodies.
1. Performance requirements for steel plates
A. Has good mechanical properties and significant deformation ability.
The mechanical properties of metal materials refer to tensile strength, yield strength, elongation, hardness, and plastic strain ratio.
High plastic strain ratio r value (anisotropic performance)
High work hardening exponent n;
High elongation δ;
Low yield to strength ratio( σ s/ σ b);
Low aging index.
B. Good surface quality
The surface of the steel plate shall not have obvious defects such as scabs, cracks, inclusions, and scratches. The interior panels of the vehicle body are allowed to have defects that do not affect formability and paint adhesion, such as small bubbles, scratches, roller marks, minor scratches, and slight oxidation colors; The outer panel must meet the quality level of FD (O5), that is, the better side of both sides must not have any defects, that is, it cannot affect the appearance quality after painting or electroplating, and the other side should meet the requirements of FB (O3).
2. Classification of steel plates
A. Divided by thickness: thick plate (above 4mm), medium plate (3-4mm), and thin plate (below 3mm)
The stamping parts of car bodies are mainly made of thin plates:
B. Classified by rolling status: hot-rolled steel plate, cold-rolled steel plate
Hot rolling is the process of softening an alloy at a temperature higher than its recrystallization temperature, and then using a compression wheel to compress the material into thin sheets or cross sections of steel billets, causing the material to deform without changing its physical properties. Hot rolled plates have poor toughness and surface smoothness, resulting in lower prices. Hot rolling is relatively rough and cannot produce very thin steel.
Cold rolling is the process of further rolling a material that has undergone the hot rolling, pitting, and oxidation removal processes at a temperature lower than the recrystallization temperature of the alloy using a roller to allow the material to undergo recrystallization. After repeated cold pressing recrystallization annealing cold pressing (2-3 cycles), the metal in the material undergoes molecular level changes (recrystallization), resulting in changes in the physical properties of the alloy. Therefore, its surface quality is good, its smoothness is high, and its product size accuracy is high. The performance and organization of the product can meet some special usage requirements.
Cold-rolled steel plates mainly include cold-rolled carbon steel plates, cold-rolled low-carbon steel plates, cold-rolled steel plates for stamping, high-strength cold-rolled steel plates, etc.
Cold-rolled carbon steel plate
Grade | Appl ication |
SPCC | For general use |
SPCD | For stamping |
SPCE SPCEN | For deep drawing |
S is the abbreviation for Steel, P is the abbreviation for Plate, the third letter C is the abbreviation for Cold, and N represents the need to ensure non aging.
Cold rolled low-carbon steel plate
Grade | Appl ication |
DC01 | For general use |
DCO3 | For stamping |
DC04 | For deep drawing |
DCO5 | For extra deep drawing |
DC06 | For super deep drawing |



